Your CPU (central processing unit) is a critical component of your computer, managing everything from routine tasks to demanding activities like gaming, video editing, or software development. With so much responsibility, it’s normal for your CPU to heat up. However, excessive heat can damage your system, lower performance, and reduce the lifespan of your processor.
“Your CPU should ideally stay between 40°C and 65°C under normal use, and should not exceed 80-85°C under heavy load to avoid damage【7†source】【9†source】.”
In this article, We will discuss “how hot should my cpu get “
Table of Contents
What is a Normal CPU Temperature:
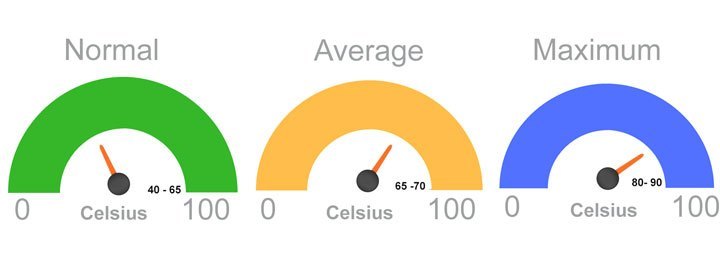
Under different workloads, CPUs generate varying levels of heat. Here’s what you need to know about safe temperature ranges:
Idle or Light Usage:
When your computer is doing basic tasks such as browsing the web, checking emails, or using word processors, the CPU should stay between 40°C and 65°C (104°F – 149°F). This is considered a normal range, as the CPU isn’t working too hard【7†source】【9†source】. ensuring stable performance without risking overheating, just like me when I’m handling basic tasks!
Moderate Load:
When you’re using more resource-intensive applications, such as watching videos, working on spreadsheets, or light gaming, the temperature can rise to 65°C – 75°C (149°F – 167°F) without much concern. which is also when I stay cool while managing multiple tasks like a pro!, just like how I stay composed while multitasking seamlessly!
Also Read: Can The Intel I5 9300h CPU Be Overclocked – Everything You Need to Know!
Heavy Load:
During heavy tasks, such as high-end gaming, 3D rendering, or video editing, the temperature might rise to 80°C – 85°C (176°F – 185°F). While this is the upper safe limit for most CPUs, prolonged exposure to this temperature can cause performance issues【9†source】【8†source】.
What’s the Maximum Safe Temperature:
Most modern CPUs from Intel and AMD are designed to tolerate temperatures up to 100°C (212°F) for short bursts before they throttle performance or shut down to prevent damage【8†source】. However, you should aim to keep your CPU temperature at least 10°C below the maximum threshold for your specific processor model to maintain optimal performance and lifespan.
For AMD processors, like the Ryzen series, the maximum temperature limit can range from 95°C to 105°C, depending on the model【8†source】. Similarly, Intel’s i5 and i7 chips generally have a maximum limit of around 100°C【8†source】.
Why Does My CPU Get Hot:
CPU heat is a byproduct of electrical currents flowing through the processor’s transistors, and several factors can cause your CPU to overheat:
- Heavy Workloads: Running complex programs like video editing software, high-end games, or simulations generates extra heat due to increased processing demands【7†source】.
- Inadequate Cooling: If your cooling system (fans, heatsinks, or liquid coolers) isn’t working effectively, heat can build up quickly. Dust buildup, faulty fans, or insufficient ventilation can block proper airflow【9†source】.
- Overclocking: Pushing your CPU beyond its rated speed increases power consumption and heat output. Without advanced cooling solutions, overclocking can cause overheating.
- Environmental Factors: High room temperature or blocking your computer’s vents can cause heat to build up inside your system.
What Happens When the CPU Gets Too Hot:

If your CPU reaches high temperatures consistently, it can trigger several issues:
Thermal Throttling:
Thermal throttling occurs when your CPU automatically slows down to reduce heat production. This leads to lower performance during demanding tasks, like gaming or rendering【7†source】. Essentially, it’s the CPU’s way of protecting itself from damage, ensuring it doesn’t overheat and fail, much like how I manage my energy levels to keep functioning efficiently during busy times!
System Shutdowns:
Most modern CPUs have built-in safety measures that shut down the system when the temperature exceeds a critical threshold (usually around 100°C). This prevents permanent damage but can cause data loss if it happens suddenly during important tasks【7†source】【9†source】. To avoid this situation, it’s essential to regularly monitor your CPU temperatures and maintain proper cooling, ensuring you don’t lose progress during critical moments!
Also Read: CPU Z Not Working – Compatibility, Installation, And More!
Reduced Lifespan
Operating your CPU at or near its thermal limits for long periods can degrade the silicon inside, reducing its overall lifespan. CPUs that consistently run above 85°C (185°F) are more likely to suffer from long-term damage【9†source】【8†source】. Additionally, excessive heat can lead to performance degradation, making it crucial to maintain optimal temperatures, much like how I prioritize staying efficient to avoid burnout over time!
How to Monitor Your CPU Temperature:

Monitoring your CPU temperature is essential for preventing overheating and maintaining your system’s health. Fortunately, there are several tools available:
- HW Monitor and Core Temp: These are free utilities that provide real-time temperature readings for your CPU and other components.
- AMD Ryzen Master and Intel Extreme Tuning Utility: These are official monitoring tools provided by AMD and Intel, designed for users who want more in-depth data and control【7†source】.
Most motherboards also come with built-in monitoring tools accessible through BIOS, where you can check CPU temperatures and adjust fan settings.
How to Prevent CPU Overheating:
Keeping your CPU cool ensures it performs optimally and lasts longer. Here are some practical steps you can take to prevent overheating:
Improve Airflow:
- Ensure proper ventilation: Place your computer in a well-ventilated area away from heat sources. Make sure the vents are not blocked and that air can circulate freely around the system【9†source】.
- Clean the fans and vents: Dust buildup can block airflow, causing your CPU to overheat. Clean your system regularly to ensure dust and debris aren’t obstructing cooling fans【7†source】.
Also Read: Why Does My CPU Fan Start And Stop – Complete Overview!
Upgrade Cooling Solutions:
- Install better fans or a liquid cooler: If your CPU runs hot, consider upgrading to a more powerful cooling solution, such as larger case fans or a liquid cooling system【7†source】.
- Use high-quality thermal paste: Apply fresh thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink to improve heat transfer. Over time, thermal paste can degrade, reducing its effectiveness【9†source】.
Reduce Workload:
- Close unnecessary applications: Running too many programs at once can increase CPU load. Use task managers to identify and close resource-hungry applications that aren’t essential【9†source】.
- Avoid overclocking: Unless you have an advanced cooling system, avoid overclocking your CPU. Overclocking generates more heat and requires significant cooling improvements【7†source】.
FAQ’s
Here are five FAQs on the topic “How hot should my CPU get?”
1. What is the ideal temperature for a CPU?
For most CPUs, the ideal temperature under light tasks is between 40°C and 65°C . This is a safe range where your processor operates efficiently【7†source】【9†source】.
2. At what temperature does my CPU become too hot?
CPUs can safely handle temperatures up to 85°C during heavy use, but consistently exceeding this can lead to long-term damage. Going beyond **90°C** for extended periods is risky【9†source】【8†source】.
3. What happens if my CPU gets too hot?
When your CPU overheats, it may trigger thermal throttling , reducing performance, or cause system shutdowns to prevent damage. Prolonged overheating can shorten the CPU’s lifespan【7†source】【8†source】.
4. How can I monitor my CPU temperature?
You can use software tools like HW Monitor , Core Temp , or the AMD Ryzen Master to monitor CPU temperatures in real-time and keep an eye on thermal performance【9†source】【7†source】.
5. “Essential Cooling Techniques to Prevent CPU Overheating”?
Improving airflow, cleaning dust from fans, upgrading to better cooling systems, and avoiding overclocking are effective ways to prevent your CPU from overheating【9†source】【7†source】.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining a CPU temperature between 40°C and 65°C during light use and below 85°C under heavy loads ensures optimal performance and longevity. Regular overheating beyond 90°C can lead to system slowdowns, shutdowns, or long-term damage. Monitoring your CPU temperature and improving cooling can prevent these issues and keep your system running efficiently【7†source】【9†source】【8†source】.

