The line “My CPU is a neural net processor” from Terminator 2 hints at the advanced AI concepts we see today; once sci-fi, neural network processors are now real, essential tech that enables devices to “think,” learn, and make decisions. From voice assistants to self-driving cars, these processors are transforming industries and pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve.
“The phrase “My CPU is a neural net processor” from Terminator 2 refers to the Terminator’s advanced, self-learning AI chip.”
In this article, We will discuss “ My CPU Is A Neural Net Processor”
Table of Contents
What is a Neural Net Processor:

At its core, a neural net processor (NNP) is a type of processing unit specialized in handling neural network computations. Unlike traditional CPUs or even GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), which perform calculations in a linear, step-by-step fashion, neural net processors are designed to handle massive amounts of data simultaneously, mimicking the way the human brain processes information.
They’re particularly useful for machine learning tasks, where algorithms benefit from the processor’s ability to learn from data patterns and continuously improve its performance.Neural net processors are often compared to the architecture of the brain. In the human brain, neurons work together to recognize patterns, such as a friend’s face or the sound of a familiar voice. Similarly, in an NNP, nodes within the network communicate in layers, “learning” relationships between data points to make predictions or decisions.
Origins of the Phrase: “My CPU is a Neural Net Processor”
When Terminator 2: Judgment Day was released in 1991, the phrase “My CPU is a neural net processor” was likely an exciting idea meant to intrigue audiences about advanced robotics and artificial intelligence. In the film, the Terminator’s neural net processor allows it to adapt and learn based on its experiences, suggesting a level of autonomy and intelligence far beyond that of most fictional robots at the time.
For audiences, this statement reflected a futuristic vision of technology—one that wasn’t far from reality. In fact, neural networks had already been in development since the 1950s, though they were relatively simplistic. It would take another two decades before we saw neural net processors capable of delivering on the vision of learning, self-improving machines as depicted in the movie.
How Neural Net Processors Work: The Building Blocks of Machine Learning
To understand how neural net processors work, we need to take a look at the principles behind artificial neural networks, or ANNs. These are frameworks that simulate the function of human neural networks, which process information in interconnected layers. Each layer in an ANN analyzes different aspects of data, allowing the processor to “learn” and adapt over time.
Also Read: LGA 2066 CPU List – Top Models And Specifications”!
Here’s a breakdown of the fundamental components:
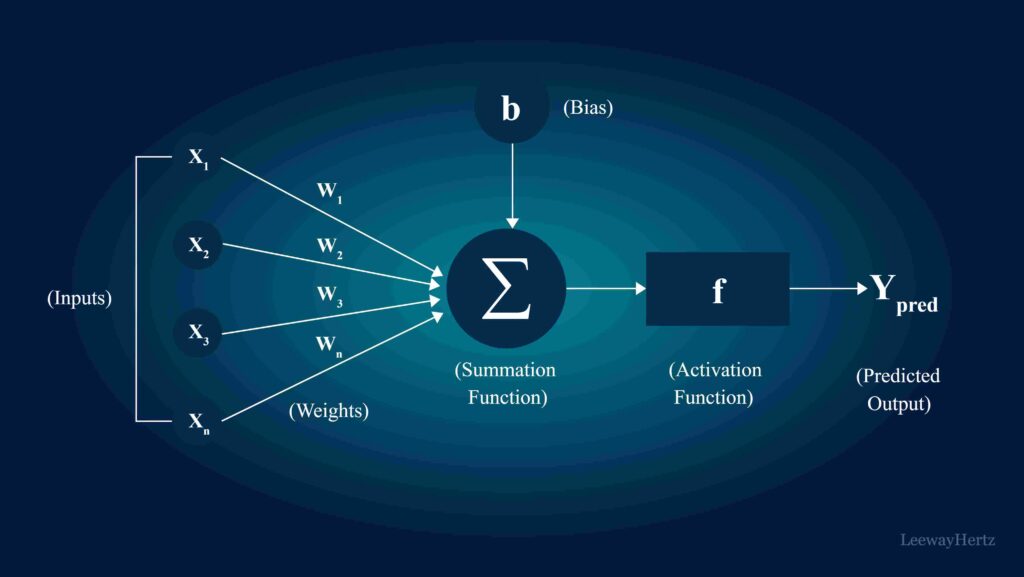
Neurons (Nodes):
In a neural network, each “neuron” is essentially a processing unit that receives inputs, processes them, and passes them to the next layer. Much like neurons in a brain, these nodes are interconnected and send information across the network.
Layers:
ANNs are organized into layers. There’s an input layer that receives raw data, one or more hidden layers where information is processed, and an output layer that provides the result. Complex models often have multiple hidden layers (referred to as “deep learning”) to allow for advanced pattern recognition.
Weights and Biases:
Each connection between nodes has a “weight” that represents the strength of the connection, allowing the network to learn which connections are more significant. Biases are constants added to the weight values, further refining the network’s accuracy.
Backpropagation and Training:
Training a neural network involves using algorithms like backpropagation to adjust weights and biases until the network accurately interprets data. This is where the “learning” happens, as the network fine-tunes itself based on errors in previous outputs.
The Importance of Neural Net Processors in Modern Technology:
Neural net processors have become the foundation for a wide range of AI applications, fundamentally changing industries like healthcare, automotive, finance, and consumer electronics. Here’s how they’re being used:
Image and Voice Recognition:
Neural processors power the image and voice recognition capabilities of smartphones, tablets, and smart speakers. For example, Apple’s Neural Engine allows Face ID on iPhones, while voice assistants like Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant use neural net processors to understand and respond to voice commands accurately.
Autonomous Vehicles:
Self-driving cars are one of the most advanced applications of neural net processors. Vehicles from companies like Tesla and Waymo are equipped with processors that interpret massive amounts of data from cameras, radar, and sensors, allowing the vehicle to make real-time decisions on the road.
Also Read: Are Most HP CPU Fansinterchangeable – A Guide To Compatibility!
Healthcare and Diagnostics:
Neural net processors are used in medical diagnostics, especially for analyzing medical images like MRIs and X-rays. By detecting patterns in medical data, these processors assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and even developing personalized treatment plans.
Gaming and Graphics:
In the gaming world, neural processors power AI-driven characters and improve graphics rendering. NVIDIA, a leader in graphics processing, leverages neural net processors to accelerate rendering and support AI-driven features in games and simulations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Natural language processing, or NLP, allows devices to understand human language and respond intelligently. Neural processors play a crucial role in NLP models used for chatbots, automated customer service, translation, and sentiment analysis, enabling machines to interpret and generate human language in real time.
Real-World Examples of Neural Net Processors:
As neural net processors become more integral to AI applications, tech companies are racing to develop more advanced versions. Here are a few notable examples:
Apple’s Neural Engine:
Apple’s custom neural engine, integrated into their A-series and M-series chips, accelerates AI tasks like Face ID, image recognition, and augmented reality. It allows Apple devices to perform tasks that were once possible only on supercomputers. making advanced technology accessible and efficient for everyday users.
Google’s Tensor Processing Unit (TPU):
Google designed TPUs specifically for AI applications, optimizing them for machine learning tasks. TPUs power Google’s deep learning models used in various services like Search, Translate, and Photos. significantly improving the performance and efficiency of these platforms while enabling real-time data processing.
Also Read: How Many Transistors In A CPU – Understanding Transistors Count In Modern Processors!
NVIDIA GPUs and Tensor Cores:
While originally built for rendering graphics, NVIDIA’s GPUs are also highly effective at machine learning tasks. Their Tensor Cores, in particular, are optimized for AI applications, making NVIDIA a popular choice for research and development in AI. enabling breakthroughs in deep learning and accelerating complex computations across various industries.
The Future of Neural Net Processors:
With machine learning and AI growing at unprecedented rates, neural net processors will play an increasingly critical role. Some anticipated future developments include:
- Greater Efficiency: Upcoming models will consume less power, making them ideal for smaller devices like wearables and mobile phones. Low-energy neural processors will allow even everyday devices to carry out AI tasks.
- Edge Computing: Instead of relying on cloud-based data centers, neural processors embedded in edge devices will enable real-time AI processing closer to where data is collected. This shift could enhance privacy, reduce latency, and improve performance.
- Neuromorphic Computing: The next frontier in AI processors is neuromorphic computing, which aims to mimic the actual structure and function of human neurons. This technology could enable processors that more closely resemble the human brain’s problem-solving abilities.
Final Thoughts:
“My CPU is a neural net processor” started as a line from a sci-fi movie but has since become a reality. Neural net processors are essential to the AI-driven world we live in today, powering everything from virtual assistants to self-driving cars. These processors are pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve, transforming how we interact with technology and envision the future.
As the technology continues to evolve, neural net processors will likely become even more capable, efficient, and integrated into our daily lives. Though we might be far from creating a self-aware machine like the Terminator, the progress of neural net processors brings us ever closer to a world where artificial intelligence complements human intelligence, making life more efficient, connected, and intelligent than ever before.
FAQ’s
1. What does “My CPU is a neural net processor” mean?
This phrase from Terminator 2 suggests that the CPU is capable of learning and adapting, similar to a human brain, by using a neural network architecture.
2. Are neural net processors real?
Yes, they are real and widely used today, especially in AI applications like image recognition, voice assistants, and autonomous vehicles.
3. How does a neural net processor differ from a regular CPU?
Unlike traditional CPUs, neural net processors are designed to handle large, complex datasets simultaneously, making them ideal for machine learning tasks.
4. What is an example of a modern neural net processor?
Examples include Apple’s Neural Engine, Google’s Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), and NVIDIA’s Tensor Cores, all of which support AI functions in various devices.
5. Can a neural net processor make decisions on its own?
While neural net processors can learn from data and make predictions, they require human-defined models and goals, so they don’t make independent decisions like a human would.
Conclusion
The phrase “My CPU is a neural net processor” from Terminator 2 foreshadowed the rise of AI-driven processors that we now use in everyday technology. Today, neural net processors power innovations in machine learning, enabling devices to “learn” and adapt in ways that mimic the human brain. As AI technology evolves, these processors will play a crucial role in shaping a smarter, more connected future.

