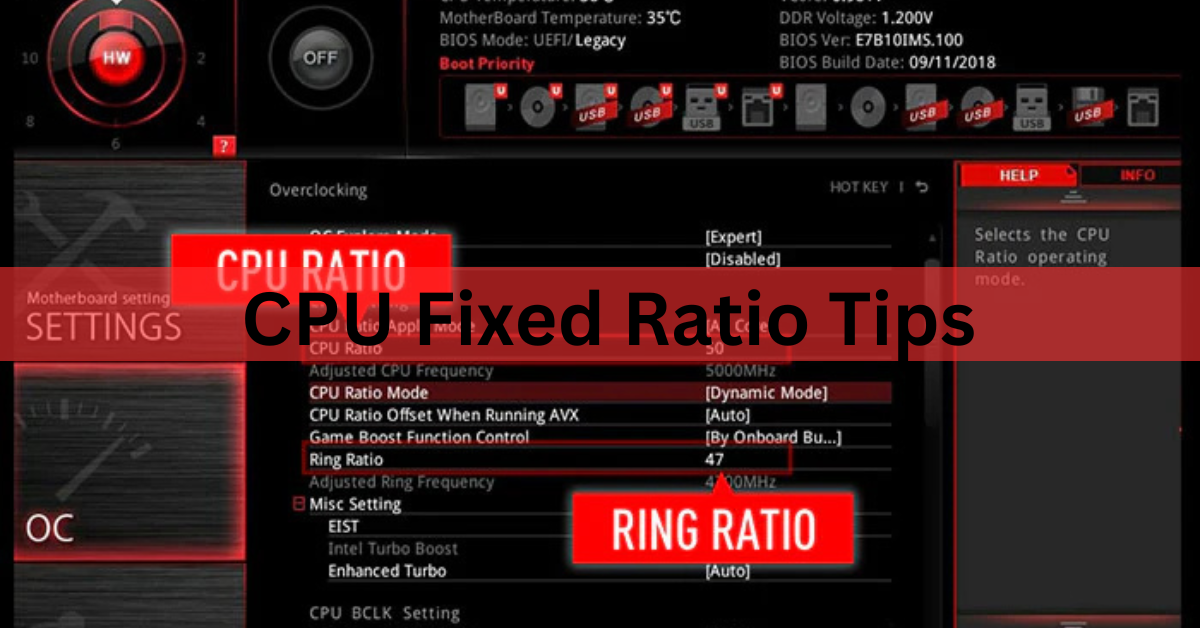
How To Keep Your CPU Running Smoother For Gaming, Video Editing & More. CPUs can be manually adjusted too for optimum performance and one such option is the CPU Fixed Ratio. cpu_fixed_ratio is tuned for better processing speed and quick system response.
“Be sure to adjust the CPU multiplier carefully to not compromise performance with temperature. Make small tweaks, observe for stability, and do not push extremes into melting or crashing the machine.”
In this article we are going to talk about “ CPU Fixed Ratio Tips ”.
Table of Contents
What is the CPU Fixed Ratio?
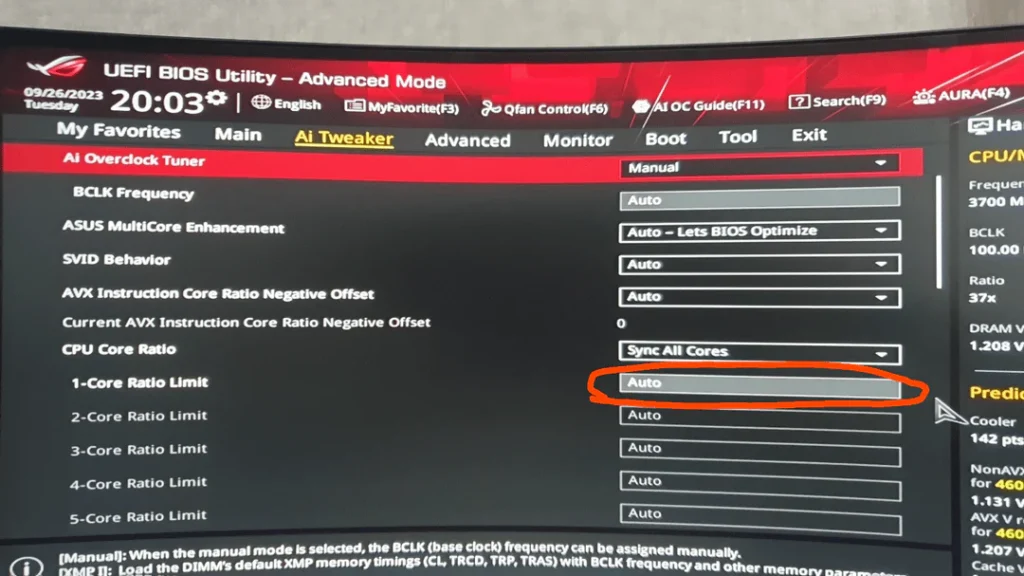
CPU Fixed Ratio (or CPU Multiplier) is a setting in your computer’s BIOS/UEFI firmware that determines how much faster the CPU can go than its base clock speed. Essentially, the Fixed Ratio is simply a multiplier that determines how much you can increase the overall clock speed of your CPU from the Base Clock (BCLK) of your processor.
For example:
For example, if your CPU has a BCLK (Base Clock) of 100 MHz, and a multiplier (Fixed Ratio) of 40 (100 which is 100 MHz x 40), your CPU is running at 4.0 GHz. A multiplication factor of 42 means your CPU will operate at 4.2 GHz.
What is The Reason for the CPU Fixed Ratio Adjustment?
The changing of the Fixed Ratio is for giving your CPU more speed or giving it less speed for power or heat reasons. Overclocking (raising the CPU clock speed) lets you extract more performance from your processor, making it work harder for demanding tasks, such as gaming or content creation. Conversely, underclocking (lowering the clock speed) saves power and lowers system heat if you don’t need the additional processing power.
Potential Pitfalls When Tweaking the CPU Fixed Ratio:
Although raising the Fixed Ratio enhances performance, it also has its consequences.
Push your CPU overclocking to.
- More heat production: Higher clock speeds require increased power and thus produce more heat. Failing to keep your CPU cool can result in thermal throttling, and under certain circumstances, an outright melt-down.
- Overloading: Overclocking your CPU can lead to system crashes, errors in applications, or even loss of data due to overheating.
- Decreased lifespan: Operating your CPU at speeds above normal for extended periods of time can decrease its lifespan. This means that you should adjust the Fixed Ratio with caution, as well as test for stability.
Also Read: Is 125W Too Much For A CPU – Explained!
Tips to Maximize CPU Fixed Ratio:
Here’s a more in-depth look at how best to tweak your CPU’s Fixed Ratio in a way that maintains a high degree of stability and longevity for your build.
Know Your CPU Specs and Limits:
Before you tweak Fixed Ratio, you need to understand what your CPU can handle. Every processor has a maximum multi (clock speed) they can safely run. Manufacturers will often list these specifications. To prevent instability, do not exceed these limits unless you’ve researched in detail or consulted with other users who’ve overclocked the same model.
- Intel processors: Intel has a selection of unlocked CPUs (with a “K” or “KF” suffix) that can be overclocked with minimal effort. For instance, an Intel Core i7-11700K or Intel Core i9-12900K.
- AMD Processors: If you’re considering AMD, there are several Ryzen processors with unlocked multipliers (like the Ryzen 5 5600X or Ryzen 9 7900X) that can be reached with overclocking.
Check online forums and databases such as Intel ARK or the AMD Product Specifications to determine what you can expect for maximum safe clock speeds specific to your CPU model.
Gradually Increase The CPU Fixed Ratio:

One of the sacred laws of overclocking is that you should bump the Fixed Ratio up bit by bit. Go directly to a high multiplier and your system crashes or becomes unstable. Rather, use these steps for a slow, measured overclocking process:
- Take it step by step: After solving the problem, raise the multiplier only by one or two steps.
- Test for stability: After each adjustment, use stress-testing software such as Prime95, AIDA64 or Cinebench to check if your system stays stable under load. If the system crashes, revert to the last working setting.
- Keep doing this: Increase the multiplier little by little, testing for stability. Whenever you reach a stable configuration, advance to the next increment.
Using and Monitor CPU Temperatures and Voltage:
If you increase your CPU’s Fixed Ratio you’re going to put added stress on your system and in turn, that means higher temperatures and more power draw. Monitor both temperature and voltage levels closely to maintain stability and avoid overheating:
- Check on the CPU temp: Apply HWMonitor or CoreTemp or similar software to monitor temp Under full load, ideally, the temperature should remain lower than 85°C. If the temperature climbs beyond that, then you likely need a better cooling solution.
- Monitor CPU voltage: If you start raising the multiplier, then your CPU may require more voltage to remain stable. Just make sure you don’t crank the voltage too high. Overvolting manifests as excessive voltage, which you proposed to the circuit, and increases risk of overheating and damaging the CPU.
First, if your system requires such extreme temperatures, you will need to improve or tone down the overclock for proper themalenization.
Stress Test for Stability:
Once you have found a fixed ratio of a higher fixed ratio that looks stable it is time to test it. Stress test tools that can simulate a heavy workload to make sure your system can run demanding applications or games without crashing.
- Prime95: One of the most popular stress test applications, Prime95 will push your CPU to its limits while looking for errors and stability.
- AIDA64: Another stress test that focuses on CPU and memory to ensure that your system can handle intense loads.
- IntelBurnTest: This tool is great to stress test your CPU, explicitly for Intel processors.
If the system survives stress tests for a few hours, you can have greater faith that your new overclock settings will “stick.” You can reduce the Fixed Ratio if the system restarts or there are errors.
Also Read; CPU How Hot Is Too Hot – Ideal Temperature Ranges Explained!
Optimize Cooling Solutions:
As explained in our previous section, overclocking can produce additional heat. When your current cooling system cannot keep up, you get throttling and system instability. Here are some suggestions to help you get the best out of your cooling system.
- Use an aftermarket, high-quality CPU cooler: Air coolers, such as the Noctua NH-D15, or liquid coolers, such as the Corsair H150i, are much better at dissipating heat.
- Increase case airflow: Make sure you have adequate airflow in your case to push hot air out and free up space for the fresh cool air to come in. This may mean installing more case fans or moving some around.
- For advanced overclockers, consider delidding: Delidding (flicking off the CPU’s integrated heat spreader) can enable superior cooling performance, but isn’t for newbies.
Change Other Settings (Memory and Power):
Not only is your CPU affected when overclocking. Overclocking the memory (RAM) and modifying the power delivery system In addition, it is also the need to adjust to ensure the stability of the legendary game.
- RAM voltage boost: You might need to increase the memory voltage or timings in order to achieve the higher CPU clock speeds.
- Increase CPU power limits: Get into BIOS/UEFI settings (or some tools) allow you increase power limits for the CPU (i.e. CPU power limits or turbo limits). Raising these to high values leaves some room for more stable overclocks at higher frequencies.
Test Long-Term Stability:
Even once you reach a stable overclock, it’s worth giving your system a reality check over time. Stress tests over shorter periods can offer useful guidance, but extended testing (like running a gaming session or rendering a video over many hours) will alert you to niggles. These longer sessions will require constant monitoring of the system to ensure everything continues to behave as expected.
FAQ’s
1. What is the CPU Fixed Ratio?
CPU Fixed Ratio (or multiplier) these affect your processor’s clock speed, multiplying the base clock to improve performance.
2. What does the CPU Fixed Ratio do?
Raising the Fixed Ratio increases the CPU’s clock speed to process tasks faster, improving performance in processor-intensive tasks.
3. Is changing of CPU Fixed Ratio safe?
Yes, that is safe as long as it is done gradually with appropriate cooling and stability testing, but too much fine tuning can result in overheating or instability.
4. How to change the CPU Fixed Ratio?
Gradually increase the multiplier, keeping an eye on temps and stress test your system to ensure stability, as well as proper cooling to prevent overheating.
5. Is My CPU Going To Get Damaged By Changing The Fixed Ratio?
Using the CPU Fixed Ratio can increase performance, but excessive overclocking without proper ventilation or voltage management can cause overheating or permanent damage.
Conclusion
Finally,tweaking the CPU Fixed Ratio is similarly sure-fire way to improve your processor performance for more power-hungry tasks! That said, before an excessive change, always check how well it goes with the stability of the system, and whether the cooling is enough to contain the damage. When done thoughtfully, you can push the speed of your CPU without sacrificing reliability and lifespan.