The CPU is the central unit that processes tasks, but it generates heat during operation. Managing its temperature is essential for stability and performance. This article covers safe temperature ranges, how to monitor heat, and tips for keeping your CPU cool.Maintaining an optimal CPU temperature helps prevent overheating, system instability, and potential damage to your hardware.
“A CPU is considered too hot if its temperature exceeds 85-90°C during heavy use, which can lead to thermal throttling or damage over time. Ideally, a CPU should run between 30-60°C during normal use and up to 80-85°C under load.”
In this article, We will discuss “Cpu How Hot Is Too Hot”.
Table of Contents
What is the Ideal CPU Temperature Range?
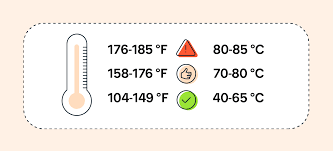
Understanding the ideal temperature for your CPU helps in determining whether it’s operating within safe limits. Temperature is typically measured in Celsius (°C), and modern CPUs are designed to work effectively within a specified range.
Idle Temperature:
When your computer is idling (i.e., not running heavy applications), the CPU temperature should be relatively low. Ideal idle temperatures are typically between 30°C to 50°C. However, this can vary based on the CPU model, ambient room temperature, and the cooling solution in place. A CPU running at idle temperatures above 50°C may indicate insufficient cooling or a high ambient room temperature.
Load Temperature:
When you run demanding programs like video games, video editing software, or render 3D models, your CPU will heat up. During these tasks, a CPU temperature range of 60°C to 80°C is typical and acceptable. These temperatures are considered safe as long as the system is not running for extended periods at the higher end of the range.
Also Read: What Is Core CPU – Exploring Their Function And Benefits!
Maximum Safe Temperature:
Modern CPUs, especially those from Intel and AMD, are designed to withstand high temperatures. 85°C to 90°C is typically considered the upper threshold for most CPUs. If your CPU reaches or exceeds these temperatures, it is in the danger zone, and you should take immediate steps to cool it down.
How Hot Is Too Hot for a CPU?
Now that we know the ideal temperature ranges, the question arises: How hot is too hot for a CPU?
Above 90°C:
If your CPU temperature consistently exceeds 90°C, it’s considered too hot. While some CPUs can handle these high temperatures without immediately failing, sustained exposure to high temperatures can cause performance throttling and, over time, significantly reduce the lifespan of your CPU. At these temperatures, your CPU may automatically throttle its speed (thermal throttling) to avoid permanent damage.
Above 100°C:
Temperatures above 100°C are considered dangerous. Most modern CPUs have a thermal throttling feature that kicks in when the temperature approaches critical levels to prevent heat damage. However, if the temperature continues to climb and exceeds 100°C, the CPU will likely shut down automatically to prevent permanent damage. If your CPU regularly hits or surpasses 100°C, there is an urgent need to address the cooling solution or hardware configuration.
Also Read: How Tight To Tighten CPU Cooler – A Complete Guide For Optimal Cooling!
Why Does Your CPU Get Hot?
Several factors contribute to CPU overheating. Understanding these can help prevent your CPU from reaching dangerous temperatures.
Overclocking:
Overclocking is the practice of running your CPU at a higher clock speed than it was designed for. While overclocking can improve performance in certain tasks, it also generates more heat. Overclocking without a robust cooling solution is a major cause of CPU overheating.
Inadequate Cooling System:
The cooling system, consisting of fans, heatsinks, or liquid cooling systems, is responsible for dissipating the heat generated by the CPU. If these systems are not working properly due to dust buildup, faulty fans, or improper installation, the CPU can overheat. Additionally, insufficient thermal paste or thermal paste degradation can also impair heat transfer.
High Ambient Temperature:
The ambient temperature of the room can have a significant impact on your CPU’s temperature. If your PC is placed in a hot environment or an area with poor airflow, it will struggle to keep the CPU cool. In contrast, cooling systems in well-ventilated, air-conditioned rooms tend to perform better.
Dust Accumulation:
Dust is one of the most common causes of overheating in computers. Over time, dust accumulates on fans, heatsinks, and vents, reducing airflow and insulating components that need cooling. This results in higher internal temperatures, leading to potential overheating issues.
Faulty Hardware:
Sometimes, the issue is with the hardware itself. If the CPU cooler is not properly seated on the processor, or if there are issues with the power supply or motherboard, the system can experience improper cooling and excessive heat buildup.
How to Keep Your CPU Cool?
Keeping your CPU within safe temperature ranges is critical for maintaining its performance and longevity. Here are some tips for keeping your CPU cool:
Upgrade Your Cooling System:
- If you’re still using the stock cooler that came with your CPU, it might be time for an upgrade. High-performance air coolers or liquid cooling systems are designed to handle the heat generated by high-demand tasks such as gaming or video editing.
- Liquid cooling, while more expensive, is often more efficient than air cooling and can keep your CPU at lower temperatures under heavy load.providing better performance and longevity for demanding tasks.
Proper Case Ventilation:
- Ensuring your case has proper airflow is essential. This can be achieved by having intake and exhaust fans in the correct positions, allowing cool air to flow in and warm air to flow out. which helps maintain consistent cooling and prevents overheating.
- You can also add more fans to the case or optimize the position of existing ones to enhance cooling. improving airflow and reducing heat buildup. This ensures better overall system performance and stability.
Also Read: Proxmox CPU Type – Host, kvm64, Qemu64 & More!
Reapply Thermal Paste:
- Over time, the thermal paste between the CPU and the heatsink can dry out, reducing its effectiveness. Reapplying high-quality thermal paste can improve heat transfer and lower CPU temperatures.
Clean Your PC Regularly:
- Dust buildup inside the case can block airflow and trap heat. Regularly cleaning your PC, especially the fans and heatsinks, ensures better cooling efficiency. preventing thermal throttling and system instability.
- Use compressed air to blow dust from hard-to-reach places, such as the CPU cooler and the fans. ensuring optimal airflow and preventing overheating. This will help maintain your system’s cooling performance over time.
Reduce Overclocking:
- If you’ve overclocked your CPU, consider reducing the clock speeds or increasing the CPU voltage limits. Overclocking will inevitably increase the temperature of your CPU, so reducing it might help to keep the temperature within safe limits.
Use Software to Monitor Temperature:
- Install temperature monitoring software such as HWMonitor, CoreTemp, or SpeedFan. These tools allow you to track your CPU’s temperature in real time and alert you if it’s reaching dangerous levels.
What to Do If Your CPU Is Overheating?
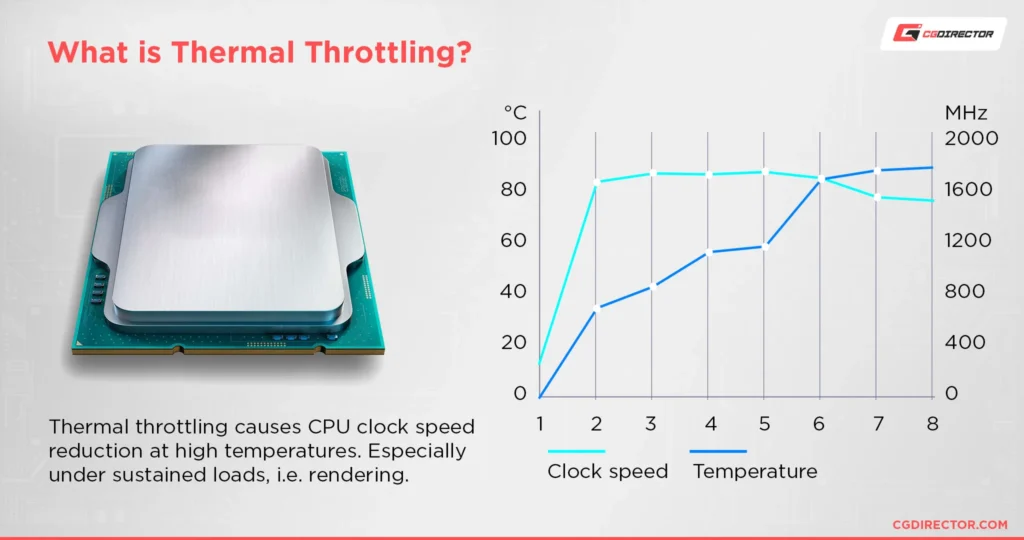
If your CPU temperature is too high, it’s essential to act quickly to prevent damage. Here’s what you can do:
Turn Off the System:
If the CPU is nearing or exceeding dangerous temperatures (above 90°C), turn off the system immediately. Allow the components to cool down before troubleshooting, and check the cooling system for any issues.
Check the Cooling System:
Ensure that the cooling fan is working correctly and seated on the CPU. If you’re using liquid cooling, check for leaks and ensure the pump is operating correctly. while also verifying thermal paste application.
Also Read: How To Calculate CPU – Step-by-Step Guide!
Clean the PC:
Open your PC case and clean out any dust that may be obstructing airflow or causing thermal issues. Pay close attention to the CPU cooler, case fans, and heatsinks. and use compressed air to reach difficult spots for thorough cleaning.
Reapply Thermal Paste:
If you haven’t already, consider reapplying thermal paste. Ensure that it’s spread evenly between the CPU and cooler. as old or degraded paste can significantly reduce cooling efficiency. leading to higher temperatures and potential system instability. This simple maintenance step can improve heat transfer and prevent overheating.
Improve Case Airflow:
Add extra case fans or reposition existing fans to improve airflow. Ensure that there is no obstruction to air intake or exhaust. Additionally, manage cable clutter to prevent airflow blockages and create a more efficient cooling environment. Proper airflow can significantly reduce the chances of overheating during heavy tasks.
Check Overclocking Settings:
If your CPU is overclocked, reduce the overclock settings to their default configuration. Running the CPU at its default clock speed will reduce heat generation. Additionally, monitor the CPU’s temperature regularly to ensure it stays within safe limits and avoid pushing the system too hard, which could lead to instability.
FAQ’s
1. How hot is too hot for a CPU?
A CPU temperature exceeding 80-90°C (176-194°F) is generally considered too hot. Prolonged exposure to temperatures above 90°C can cause damage.
2. What is the ideal temperature for a CPU?
The ideal range is usually between 30-50°C (86-122°F) during regular use. Under heavy load, temperatures can rise to 60-70°C (140-158°F).
3. Can a CPU overheat from gaming or heavy tasks?
Yes, intense tasks like gaming or rendering can push temperatures higher. It’s important to ensure good cooling.
4. How can I reduce my CPU temperature?
Improve airflow in your PC case, clean dust from fans, apply high-quality thermal paste, or upgrade your cooling system.
5. What happens if my CPU gets too hot?
If a CPU gets too hot, it may throttle performance or shut down to prevent permanent damage. Overheating over time can shorten its lifespan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining an optimal CPU temperature is crucial for system stability and performance. Temperatures exceeding 85-90°C can cause damage and shorten the lifespan of your CPU. Proper cooling, dust management, and monitoring are essential to keep your CPU running safely within the ideal temperature range.