Calculating CPU performance is essential for anyone looking to understand their system’s capabilities, whether you’re building a new PC, upgrading components, or simply wanting to optimize your current setup. Understanding these metrics can help you achieve better performance for gaming, content creation, and other CPU-intensive tasks.
“To calculate CPU performance, use benchmarks like PassMark or Cinebench that assess speed and efficiency. You can also consider factors such as clock speed, core count, and architecture.”
In this article, We will discuss “ How to Calculate CPU .“
Table of Contents
Understanding CPU Performance:
CPU performance is typically measured by how quickly and efficiently it can execute tasks. Several factors influence performance, including clock speed, core count, cache size, and the architecture of the processor. By understanding these components, you can better assess how to calculate and compare CPU performance across different models.
Key Metrics for CPU Calculation:
Clock Speed (GHz):
Clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), indicates how many cycles per second the CPU can execute. A higher clock speed generally means better performance, but it’s not the only factor. It’s essential to consider how well the CPU architecture handles those cycles. For instance, a newer architecture with lower clock speeds can outperform an older one with higher clock speeds.
Core Count:
Modern CPUs come with multiple cores, allowing them to handle more tasks simultaneously. Each core can manage its own thread, which is beneficial for multitasking and running applications designed to utilize multiple threads effectively. For example, a quad-core processor can handle more tasks simultaneously compared to a dual-core processor, making it ideal for gaming, video editing, and other CPU-intensive tasks.
Also Read: Is 40c Good For CPU – Understanding Safe Temperature Ranges!
Benchmark Scores:
Benchmarking tools provide standardized tests to evaluate CPU performance under various conditions. Popular benchmarking software includes. These scores are derived from various tests that simulate real-world workloads, providing insights into how well a CPU can handle different tasks.By understanding these scores, users can make informed choices about upgrades and configurations.
Cinebench:
Tests CPU rendering capabilities and provides a score based on performance. It simulates real-world rendering tasks, which is particularly useful for evaluating performance in creative applications. This tool is widely used in the creative industry to benchmark CPUs for tasks like 3D modeling and animation, helping users select the best hardware for their specific needs.
PassMark:
Offers a comprehensive performance score based on several tests, including CPU mark, integer, and floating-point performance. This tool helps to provide a holistic view of CPU performance across different workloads.
Thermal Design Power (TDP):
TDP indicates how much heat a CPU generates under typical load conditions, which can also relate to its performance and efficiency. Lower TDP often means better energy efficiency, allowing for quieter operation and less strain on cooling solutions. Understanding TDP is crucial for selecting appropriate cooling solutions and ensuring optimal performance without overheating.
Cache Size:
The CPU cache is a small amount of high-speed memory located on the processor chip itself. Larger cache sizes allow for quicker data access and can significantly impact performance, particularly in tasks that require rapid data retrieval. L1, L2, and L3 caches each have different sizes and speeds, with L1 being the fastest but smallest, and L3 being larger but slower.
How to Calculate CPU Performance:
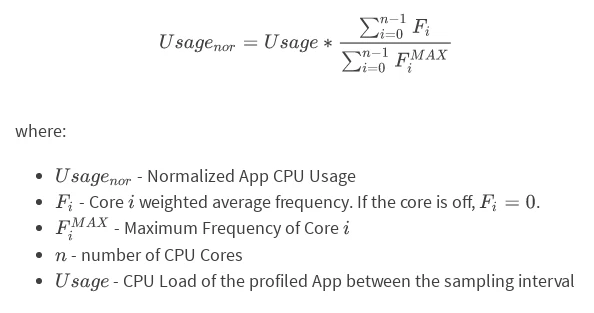
To calculate CPU performance, you can follow these steps:
Use Benchmarking Tools:
Download Benchmarking Software:
Install a reliable benchmarking tool such as Cinebench, PassMark, or Geekbench on your system. These tools are designed to provide a standardized way to assess performance. These applications not only evaluate CPU performance but also offer insights into other system components, giving you a comprehensive view of your hardware’s capabilities.
Run the Benchmark:
Follow the software instructions to conduct the tests. The benchmarking software will run various workloads on your CPU, evaluating different aspects of performance, including single-threaded and multi-threaded tasks. Be prepared for the benchmarking process to take several minutes, as it runs various workloads to thoroughly evaluate your CPU’s capabilities.
Also Read: Can The Intell I5 p300 h CPU Be Overclocked – Understanding Its Limitations!
Review Your Score:
After the benchmark completes, check your score. This score represents your CPU’s performance relative to other processors, allowing you to gauge its capabilities effectively. You can compare your scores to online databases to see how your CPU stacks up against others. Understanding where your CPU stands in relation to others can help you identify potential upgrade paths or optimizations for your system
Analyze Clock Speed and Core Count:
Check Specification:
Look up your CPU’s specifications online or use tools like CPU-Z to find the clock speed and core count. Understanding these specs will help you interpret the benchmark scores more effectively. These specifications are critical for understanding the performance metrics associated with your CPU and can highlight areas for potential improvement.
Calculate Performance:
While there’s no direct formula for calculating overall CPU performance, you can consider clock speed and core count together. For example, a CPU with 4 cores at 3.5 GHz might perform better in multi-threaded tasks compared to a dual-core CPU at 4.0 GHz. You can also consider the IPC (Instructions Per Cycle) of the architecture, as this will give a clearer picture of overall performance.
Consider Real-World Performance:

Test Real-World Applications:
Run applications or games that are CPU-intensive and monitor the performance impact. Comparing benchmark scores to actual performance in these applications will give you a practical understanding of how your CPU handles real-world tasks.This hands-on approach helps you assess whether your CPU meets your needs for specific tasks, such as gaming or video editing.
Use Monitoring Software:
Tools like HWMonitor can provide real-time data on CPU usage, temperature, and power consumption during these tests. Monitoring these metrics helps identify any performance bottlenecks and ensures that your CPU operates within safe thermal limits. By keeping an eye on these metrics, you can make informed adjustments to your system for optimal performance and longevity.
Also Read: Do I Need Two CPU Power Cables – A Complete Guide!
Assess CPU Temperature and Power Consumption:
Check Operating Temperatures:
Use temperature monitoring tools to ensure your CPU operates within safe temperature ranges during benchmarking and heavy workloads. Ideal temperatures vary by processor model, but generally, you want to keep your CPU below 85°C under load. Keeping your CPU at optimal temperatures not only improves performance but also extends the lifespan of your hardware.
Evaluate Power Consumption:
Understanding how much power your CPU consumes under different workloads can also inform your calculations. High-performance CPUs often consume more power, which may require better cooling solutions and power supplies. By evaluating power consumption, you can ensure that your system’s components are well-matched, preventing potential bottlenecks and enhancing overall stability.
FAQ’s
Here are five FAQs with short answers related to “How to Calculate CPU”:
1. What tools can I use to calculate CPU performance?
You can use benchmarking tools like Cinebench, PassMark, and Geekbench to assess and calculate CPU performance through standardized tests.
2. Understanding Benchmark Scores?
Benchmark scores represent the CPU’s performance relative to other processors; higher scores indicate better performance. You can compare your scores to online databases for context.
3. What factors should I consider when calculating CPU performance?
Key factors include clock speed (GHz), core count, cache size, thermal design power (TDP), and real-world application performance.
4. Is clock speed the only metric that matters?
No, while clock speed is important, you should also consider core count and the CPU architecture, as these factors significantly impact overall performance.
5. How can I ensure my CPU is performing optimally during calculations?
Regularly monitor CPU temperatures and power consumption using tools like HWMonitor, and ensure your cooling solution is effective to prevent thermal throttling.
Conclusion
In conclusion, calculating CPU performance requires a multifaceted approach that includes benchmarking, analyzing clock speed and core count, and considering real-world application performance. By utilizing reliable benchmarking tools and monitoring CPU metrics, you can gain valuable insights into your processor’s capabilities. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions when optimizing or upgrading your system for specific tasks.

