Undervolting your CPU in Gigabyte BIOS helps reduce power consumption and heat, improving system efficiency without affecting performance. This process involves lowering the CPU voltage through the BIOS settings, which can result in a cooler, quieter, and more energy-efficient system. Additionally, undervolting can extend the lifespan of your hardware by reducing wear and tear caused by excessive heat and power draw.
“To undervolt a CPU in Gigabyte BIOS, navigate to the BIOS settings, find the “CPU Voltage” or “Vcore” setting, and reduce it slightly in small increments. Save and exit the BIOS, then test system stability.”
In this article, We will discuss “ How To Undervolt Cpu Gigabyte Bios”.
Table of Contents
What is Undervolting and Why Should You Do It?
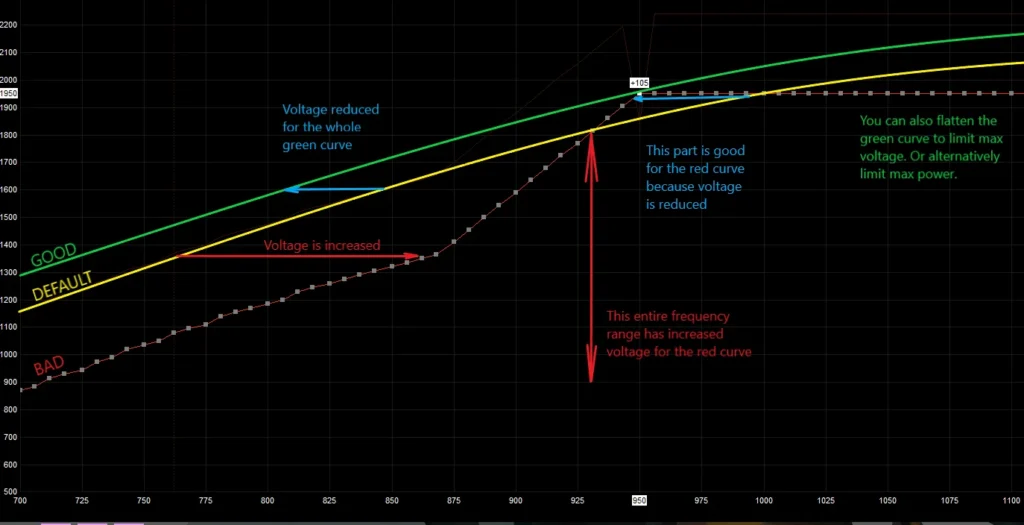
Undervolting is the process of reducing the voltage supplied to the CPU while maintaining stable performance. Unlike overclocking, which increases voltage to achieve higher clock speeds, undervolting lowers the voltage to decrease power consumption and heat generation. This is a beneficial strategy for a variety of reasons:
- Lower CPU Temperatures: By lowering the voltage, the CPU generates less heat, which leads to cooler system temperatures. This is especially beneficial for users who are concerned about thermal throttling or running resource-intensive applications.
- Enhanced Power Efficiency: Undervolting reduces your system’s overall power consumption. This not only lowers electricity bills but also makes your system more environmentally friendly.
- Longer Component Lifespan: CPUs that run at lower voltages generate less heat, which can help reduce the wear and tear on your hardware. Over time, this can help extend the lifespan of your processor and other components, making undervolting an excellent long-term strategy.
- Quieter Operation: Since undervolting reduces the heat output of your CPU, your cooling system (fans or liquid cooling) will not need to work as hard, leading to quieter operation.
Benefits of Undervolting Your CPU in Gigabyte BIOS:
- Better Thermal Management: By undervolting, your CPU produces less heat, which in turn improves the thermal performance of your PC.This leads to quieter operation, as the cooling system doesn’t need to work as hard to maintain safe temperatures.
- Enhanced Stability: Running your CPU at a lower voltage often leads to improved stability, especially when combined with proper cooling.This can result in fewer crashes and a more consistent performance, even during heavy workloads or extended use.
- Lower Fan Noise: Since your system runs cooler, your cooling fans may run at lower speeds, producing less noise overall.This contributes to a quieter computing experience, making it ideal for those who prefer a noise-free environment.
How to Undervolt CPU in Gigabyte BIOS:
Enter the BIOS Setup:
The first step in undervolting your CPU is to enter the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System). Restart your computer and press the Delete key (or F2 on some systems) as soon as the system powers on. This will bring you to the BIOS screen. Gigabyte motherboards typically feature an easy-to-navigate BIOS with multiple options for tweaking system settings.
Also Read: Why Is My CPU Fan So Loud – Common Causes And Solutions!
Switch to Advanced Mode:
Once you’re in the BIOS, you may find that you’re in the Easy Mode, which is a simplified interface for basic adjustments. To make more detailed changes, including undervolting, switch to Advanced Mode. You can do this by pressing F2 or clicking on the “Advanced Mode” button located at the bottom of the BIOS screen.
Locate the CPU Voltage Settings:
In Advanced Mode, navigate to the Tweaker or Overclocking tab (the exact name of this tab can vary depending on your specific motherboard model). Look for the CPU Voltage or Vcore settings. This is where you’ll be able to adjust the voltage sent to your CPU.
- On some motherboards, you may find CPU Voltage, Vcore, or CPU Core Voltage Offset settings, which allow for more granular adjustments.
- Gigabyte BIOS typically has two main ways to adjust voltage: Manual Mode and Offset Mode. Each method has its own advantages, depending on how much control you want over the voltage.
Adjust the CPU Voltage:
Now that you’ve located the CPU voltage settings, it’s time to adjust the voltage.
- Manual Mode: In this mode, you can directly input a value for your CPU voltage. Start by decreasing the voltage by a small amount, around 0.05V (50 mV) from the default setting. This will help prevent system instability while allowing you to test whether your CPU can handle the new, lower voltage.
- Offset Mode: If you prefer a more automated method, the Offset Mode allows you to set a negative offset to reduce the voltage across all cores. For example, a -0.05V offset will reduce the voltage by 0.05 volts, making it easier to make fine adjustments.
Save and Exit BIOS:
After adjusting the CPU voltage, save your changes. To do this, press F10 or navigate to the “Save & Exit” option in the BIOS menu. Confirm that you want to save the changes and reboot your computer. Your system will now run at the new undervolted settings.
Test System Stability:
After booting into your operating system, it’s essential to check your system’s stability. Use stress testing tools like Prime95, AIDA64, or IntelBurnTest to push your CPU to its limits and see if it can handle the workload at the lower voltage. You can also monitor system temperatures and performance using tools like HWMonitor or CoreTemp to ensure the undervolt has resulted in lower temperatures and power consumption.
If your system experiences crashes, freezes, or blue screens, it’s likely that the undervolt is too aggressive. In this case, return to the BIOS, and increase the voltage slightly, then test again. It’s crucial to make small adjustments and test thoroughly to find the right balance between stability and performance.
Tips for Safe and Effective Undervolting:
- Start Slowly: When undervolting, always start with small adjustments (around 0.05V) and test stability each time. This helps you find the optimal voltage without causing instability.
- Monitor Temperatures: After undervolting, closely monitor your system’s temperature to ensure it stays within safe limits. Use temperature monitoring tools like HWMonitor or CoreTemp to track your CPU’s temperature during heavy usage.
- Stability Testing Is Key: Always run stress tests to confirm your system can handle the new voltage settings under load. If your system crashes, increase the voltage slightly and retest.
- Use Offset Mode for Simplicity: If you’re not comfortable adjusting manual voltage settings, use the Offset Mode to apply a uniform reduction across all cores. This mode is often safer and easier for beginners.
- Document Your Settings: Keep track of the changes you make to the voltage and other settings in case you need to revert them or troubleshoot any issues later.
Also Read: What Are The Registers In A CPU – Understanding Their Role And Importance!
Common Issues When Undervolting and How to Solve Them:
- System Instability: If your system crashes or becomes unstable after undervolting, it may be due to the voltage being too low. In such cases, return to the BIOS, increase the voltage slightly, and test again.
- Overheating: While undervolting should help reduce temperatures, inadequate cooling can cause overheating issues. Ensure that your cooling solution (fans or liquid cooling) is sufficient for the system’s needs.
- Performance Drop: In rare cases, undervolting too much may result in noticeable performance drops. If you observe a significant decrease in performance, slightly increase the voltage until you achieve the desired balance.
FAQ’s
1. What is CPU undervolting?
CPU undervolting is the process of reducing the voltage supplied to the CPU to lower power consumption, heat generation, and improve overall system efficiency.
2. How do I access BIOS on a Gigabyte motherboard?
To access BIOS, restart your computer and press the Delete or F2 key during boot-up.
3. Is it safe to undervolt my CPU in Gigabyte BIOS?
Yes, it is safe if done carefully, starting with small voltage reductions and testing stability to ensure your system runs smoothly.
4. Will undervolting affect my CPU’s performance?
Undervolting should not affect performance if done correctly, but excessive undervolting can lead to system instability or crashes.
5. How do I test if my CPU undervolt is stable?
Run stress tests like Prime95 or IntelBurnTest and monitor system temperatures to ensure stability after undervolting.
Conclusion
Undervolting your CPU in Gigabyte BIOS is an effective way to improve system efficiency by reducing power consumption and heat. By making small adjustments to the CPU voltage, you can achieve a cooler, quieter, and more energy-efficient system without sacrificing performance. Always test for stability after each change to ensure your system runs smoothly and remains reliable.

