If you’ve encountered the message “OC is not supported CPU” while trying to overclock your system, it means that your CPU or motherboard does not allow overclocking. Overclocking is a method of boosting your processor’s speed beyond its default limits, but not all CPUs and motherboards are designed to handle this. Understanding your hardware’s limitations is key to determining the best performance options for your system.
“If your system shows “OC is not supported” for your CPU, it means your processor doesn’t support overclocking. Only specific CPUs, such as Intel’s “K” series and AMD’s Ryzen models, are designed for overclocking capabilities.”
In this article, We will discuss “oc is not supported CPU”
Table of Contents
What Does “OC is Not Supported” Mean?
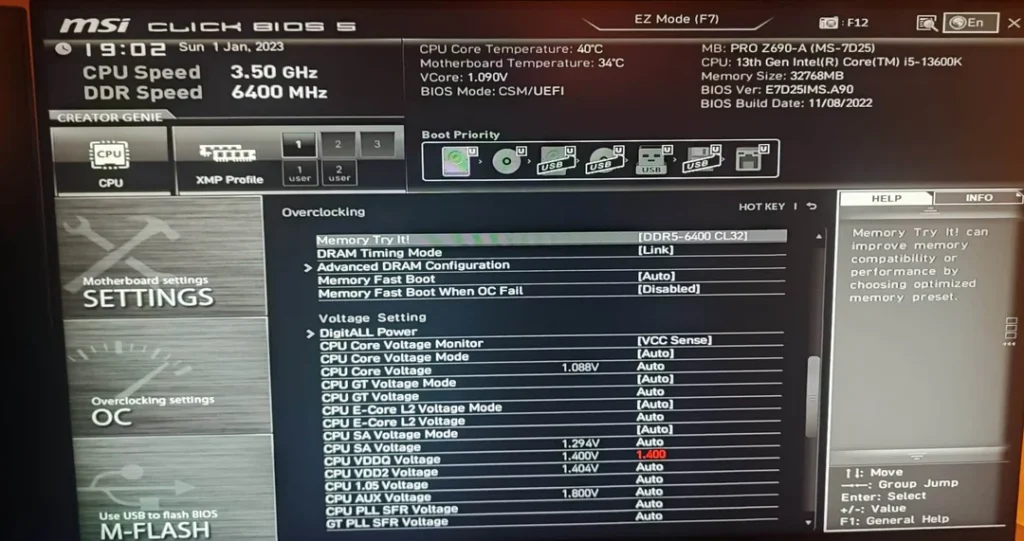
The “OC is not supported” message means that your system’s CPU or motherboard cannot perform overclocking. Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock rate of a computer’s CPU to run faster than its official speed. It’s an advanced technique used to push the hardware to its limits, but not all processors or motherboards are equipped to handle it.
Why Certain CPUs Don’t Support Overclocking:
Locked Processors:
Many processors come locked by default. A locked CPU cannot exceed its base clock speed, no matter what settings you try to tweak. Manufacturers like Intel and AMD release specific unlocked versions designed for overclocking. If you have a locked processor, you’ll see the “OC is not supported” message. Many CPUs are locked by default, preventing overclocking to maintain stability and efficiency.
Motherboard Restrictions:
Even with an unlocked CPU, your motherboard must support overclocking. Certain chipsets on motherboards do not allow users to modify clock speeds, limiting any overclocking attempts. This is common in budget or office-oriented systems. Some motherboards do not support overclocking, even with unlocked CPUs, limiting your ability to boost performance.
Also Read: How To Split 8 Pin CPU Connector – Benefits And Techniques!
BIOS or Firmware Limitations:
Sometimes, even if your CPU and motherboard support overclocking, you might not be able to find the option because of outdated BIOS or firmware. Newer versions of BIOS may unlock features that were previously unavailable. Outdated BIOS or firmware can restrict overclocking features, preventing users from accessing necessary settings to increase clock speeds.
Which CPUs Support Overclocking?
When it comes to overclocking, both Intel and AMD have specific CPU models designed for this purpose. If you’re unable to overclock your CPU, it may be because you have a locked model. Here’s an overview of which CPUs support overclocking and why some don’t.
Intel Processors:
Intel offers two types of consumer CPUs: locked and unlocked. Unlocked CPUs allow overclocking and are designated by a “K” or “X” suffix.
- Unlocked CPUs (Overclockable): Processors like the Intel Core i5-10600K, i7-10700K, and i9-11900K are examples of CPUs that support overclocking. These processors are specially designed for enthusiasts and gamers who want to push their performance further.
- Locked CPUs (Non-Overclockable): Standard models such as the Intel Core i5-11400 or i7-11700 cannot be overclocked. These processors are designed for stability and energy efficiency rather than pushing performance limits. If you have a locked CPU, you won’t be able to overclock it, and the “OC is not supported” message will appear.
AMD Processors:
AMD is more generous with overclocking support compared to Intel. Most of AMD’s Ryzen processors are unlocked, even at the mid-range level.
- Unlocked CPUs (Overclockable): Most Ryzen CPUs, from the Ryzen 3 3300X to the high-end Ryzen 9 5900X, support overclocking. AMD’s overclocking-friendly design makes it an attractive choice for enthusiasts who want more control over their CPU’s performance.
- Locked CPUs (Non-Overclockable): Some older AMD models, like certain Athlon processors or early-generation Ryzen chips, may not support overclocking. Additionally, APUs (AMD processors with integrated graphics) often have limited overclocking potential.
Why Overclocking Matters:

Overclocking can provide a significant performance boost, particularly in graphics-intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and 3D rendering. Here are some scenarios where overclocking can make a noticeable difference: Overclocking can enhance performance for demanding applications and gaming, providing a competitive edge by maximizing hardware capabilities.
Gaming Performance:
Overclocking can increase frame rates, reduce lag, and smooth out gameplay, especially in CPU-bound games. This is critical for users playing at higher resolutions or using high-refresh-rate monitors. Overclocking can significantly improve frame rates and responsiveness in games, leading to a smoother and more immersive gaming experience.
Video Editing and 3D Rendering:
For content creators, overclocking can reduce rendering times and make video editing tasks much faster. It allows applications like Adobe Premiere or Blender to utilize the CPU more efficiently. Overclocking boosts processing power, allowing for faster rendering times and improved performance in resource-intensive video editing and 3D modeling tasks.
Also Read: Env Node Bad Cpu Type In Executable – Step By Step!
Multitasking and Productivity:
In tasks that require multiple applications running simultaneously, an overclocked CPU can handle more processes at once without slowing down. Overclocking can enhance system responsiveness, enabling smoother multitasking and improved performance in demanding productivity applications.
How to Check if Your CPU Supports Overclocking:
If you’re unsure whether your CPU can be overclocked, here are some simple ways to check:
Identify Your CPU Model:
First, find out what CPU model you have. On Windows, you can do this by opening Task Manager, selecting the Performance tab, and viewing the CPU name. You can also use third-party programs like CPU-Z to get more detailed information. Knowing your CPU model helps determine its overclocking capabilities and whether it is locked or unlocked for performance adjustments.
Look Up Manufacturer Specs:
Once you have your CPU model, visit Intel’s or AMD’s official website. Look up the specifications for your CPU, and see if it is labeled as unlocked (Intel) or overclockable (AMD). If it’s a K-series Intel CPU or an unlocked Ryzen processor, you’re good to go. Reviewing the manufacturer’s specifications provides detailed information about your CPU’s capabilities, including its overclocking potential and supported features.
Check Motherboard Compatibility:
Even with an overclockable CPU, your motherboard also needs to support overclocking. For Intel, you’ll need a motherboard with a Z-series chipset (like Z490 or Z590). For AMD, motherboards with B-series or X-series chipsets (such as B450 or X570) support overclocking. Ensuring your motherboard supports overclocking is crucial, as not all boards provide the necessary settings or features for adjusting CPU clock speeds.
What to Do If Overclocking Isn’t Supported:
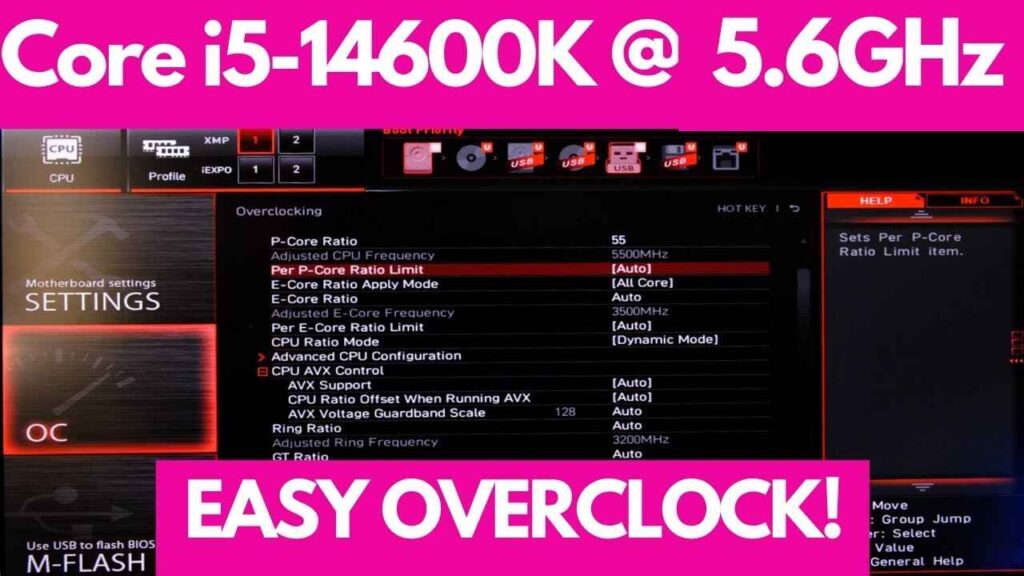
If you find out that your CPU or motherboard doesn’t support overclocking, don’t worry. There are still ways to optimize your system’s performance without overclocking: consider optimizing your system settings, upgrading your hardware, or using performance-enhancing software to improve performance.
Upgrade Your CPU and Motherboard:
If overclocking is crucial for your needs, consider upgrading to an overclockable CPU and a compatible motherboard. For Intel users, this means investing in a K-series CPU and a Z-series motherboard. For AMD users, choose a Ryzen processor and a motherboard that supports overclocking.
Optimize Your BIOS Setting:
Even without overclocking, you can still adjust some settings in your BIOS to improve performance. Intel’s Turbo Boost and AMD’s Precision Boost technologies allow the CPU to automatically increase its clock speed when needed.
Also Read: Can I Use Higher Frequency Ram Than CPU-Comprehensive Guide!
Improve Cooling Solutions:
One of the main reasons CPUs don’t perform optimally is overheating. If your CPU runs too hot, it will throttle performance to prevent damage. By improving your cooling system—such as adding more case fans or using a liquid cooler—you can help your CPU maintain higher performance for longer.
Optimize Your Software:
Adjusting system settings and disabling unnecessary background tasks can help free up resources for your CPU to handle more demanding tasks. Additionally, keeping drivers and software updated can ensure that your hardware performs as efficiently as possible.
Upgrade Your Power Supply:
An insufficient power supply can limit your system’s performance, especially if you’ve upgraded other components. Make sure your power supply can handle the demands of your CPU, GPU, and other hardware.
FAQ’s
Here are 5 FAQs with short answers for “OC is not supported CPU”:
1. What does “OC is not supported CPU” mean?
It means your CPU or motherboard does not support overclocking, which prevents adjusting the clock speed beyond the factory settings.
2. Why can’t I overclock my CPU?
You likely have a locked CPU or a motherboard that doesn’t support overclocking, both of which limit the ability to increase clock speeds.
3. How can I check if my CPU supports overclocking?
Check the CPU model number. Unlocked Intel CPUs have a “K” or “X” suffix, while most AMD Ryzen CPUs are unlocked.
4. Can I enable overclocking with a software update?
No, overclocking requires compatible hardware, like an unlocked CPU and a supporting motherboard, not just software or BIOS updates.
5. What are my options if overclocking isn’t supported?
You can upgrade your CPU and motherboard, optimize cooling, or adjust system settings for better performance without overclocking.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the “OC is not supported CPU” message indicates that your CPU or motherboard doesn’t support overclocking. This could be due to a locked processor or an incompatible motherboard. While overclocking may not be an option, upgrading hardware or optimizing system settings can still improve your system’s performance.

